Hi colleagues,
TRM has several customizations at the organizational level. These configurations are necessary before we can create any deal in TRM. The majority of these are obligatory, but a few of them are not. It is possible to conclude that these configurations are the initial step in TRM.
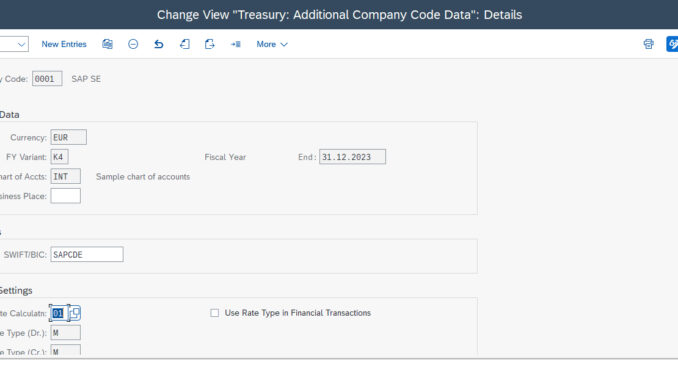
A- Company code Additional data
SPRO> Financial Supply Chain Management> Treasury and Risk Management> Transaction Management> General settings> Organization> Company code additional data
Here we define additional data for the company codes we user. General Settings, Enter the SWIFT code for the company code here, Settings for exchange rates:
Enter the rate calculation indicator for your exchange rate translations in the current company code. The rate calculation indicator specifies the debit and credit rate categories and is only used in the securities and loans areas.
Settings for the securities area:
- Specify whether or not short sales are permitted.
- Define a price type for security prices that you will use for evaluations.
Settings for loans
Enter the factory calendar that the system should use for this company code in loans management.
You can specify the factory calendar that the system should use per default for each condition type and group when you enter a condition item. For more information, see the implementation guide (IMG) for loan management in the IMG activity, Define Condition Groups, in view Assign Condition Types to Condition Groups. If you have not specified a factory calendar here per condition group for a condition type, the system uses the factory calendar that you have defined in this IMG activity for the company code.
Settings for regulatory reporting:
Specify if regulatory reporting is active. If so, define additional data for regulatory reporting.
Requirements
- You have already created the relevant FI company codes.
- You have activated Financial Assets Management for all relevant FI company codes (checkbox ‘Financial Assets Management’ active).
- You have already defined the calculation indicator for exchange rate translation.
Company code data is automatically fetch we cannot change it here
B- Define Portfolio
SPRO> Financial Supply Chain Management> Treasury and Risk Management> Transaction Management> General settings> Organization> Define Portfolio
Define portfolios per company code. We use the portfolios as an organizational element to group various financial transactions for reporting purposes.
Use
- If you create a financial transaction, you assign the portfolio on the Administration tab.
- You can use the portfolio as a selection criterion.
- You can use the portfolio as an analysis characteristic in risk management.
Activities
- Choose the company code.2. Choose New Entries.3. Enter an alphanumeric ID and a description for the portfolio.4. Save your entries.
C- Define Trader
SPRO> Financial Supply Chain Management> Treasury and Risk Management> Transaction Management> General settings> Organization> Define Trader
In this step, you define your traders for each company code.
Activities
Define a name for each trader using New entries.
D- Define User Data
SPRO> Financial Supply Chain Management> Treasury and Risk Management> Transaction Management> General settings> Organization> Define User Data
Similar to the definitions you make for user parameters, you can make the following individual settings per user here:
- The following abbreviations are available when you create transactions: t for 1,000 (one thousand) and m for 1,000,000 (one million). You can define different abbreviations if you wish: for example, x for 1,000 and y for 1,000,000.
- You can make settings to determine whether and how a workday check takes place.
- You can determine whether there will be an exchange rate input or SWAP input check or both.
The input check compares the values entered with the current market data in the rate tables. You receive warning messages if there are serious inconsistencies. •You can define a default value for the trader name.
Activities
- Choose New entries to enter definitions for a user name.2. Make the required entries. To determine values, use the F1/F4 Help.3. Save your entries.
Further Notes
You will see which parameter IDs are available to you in Treasury from the following table.
You can use parameter IDs to define a default value for certain fields for each user. This facilitates and accelerates input if a user is basically only working in one company code, for example, or only one market data provider is being used.
You can enter default values for parameter IDs in the application via System -> User profile -> Own data.
E- Define Valuation Area
SPRO> Financial Supply Chain Management> Treasury and Risk Management> Transaction Management> General settings> Accounting> Organization> Define Valuation Area
We define all of the valuation areas that you require. You define valuation area 001, which is the paying valuation area, and all other parallel valuation areas.
Example
001 HGB (= paying valuation area)
002 US GAAP
003 …
Activities
- Choose New Entries.2. Assign a 3-character abbreviation and a long name for the valuation area.3. Save your entries.
F- Define Accounting Code
SPRO> Financial Supply Chain Management> Treasury and Risk Management> Transaction Management> General settings> Accounting> Organization> Define Accounting Code
In this menu option we define Accounting codes and assign the corresponding FI company codes to them in a 1:1 relationship.
Activities
- Choose ‘New entries’.2. Assign a 4-character abbreviation and a long name for the accounting code.3. Assign a company code.4. Save your entries.
G- Assign Accounting code to Valuation Area
SPRO> Financial Supply Chain Management> Treasury and Risk Management> Transaction Management> General settings> Accounting> Organization> Assign Accounting code to Valuation Area
We assign the valuation areas to accounting codes. Also make settings for the FI update and for valuation.
Requirements
If you want to use special ledgers to represent the parallel valuation areas, you must define the special ledgers before you make the assignment in this IMG activity. The special purpose ledgers are a standard FI function.
You set up special purpose ledgers in FI Customizing by choosing Financial Accounting -> Special Purpose Ledger.
Procedure:
- Choose Financial Accounting -> Special Purpose Ledger -> Basic Settings -> Perform Preparation, and activate the indicators Local ledgers (company codes) and Several languages.2. To create the required ledgers, choose Financial Accounting -> Basic Settings -> Master Data -> Maintain Ledgers.a) Choose Create Ledger.b) Enter a short and long text for the special ledger.c) In the Summary table field, enter “TRACTSLT”.d) In the Application field, enter “Financial Accounting”.e) In the Subapplication field, enter “Special Purpose Ledger”.f) In the Valuation field, enter “Legal Valuation”.g) Set the following indicators in the Further Settings section:- Ledger Post. Allowed- Write Line Items- Debit/Credit- Set up balance c/fh) In the Stored Currencies section, select the Transaction Currency, and the company code currency as the 2nd Currency. You can also select a 3rd Currency.i) Assign the company code using the pushbutton Assign comp.cd/comp . If you want to use a separate chart of accounts for the company code (Validation type “9”), see SAP Note 7627.j) Assign the activity “RFBU” using the pushbutton Assign Activity.
Assign a field movement in the Field movement field using the F4 Help. An error message appears, since the appropriate field movement does not yet exist. You can create a field movement from within the error message. Alternatively, you can use the Field movement pushbutton to branch to the rule definition.
Give the field movement a name, for example, “TRM1 Field Movement for TRM”. In the table, enter “RACCT” in the Receiver field column “ACCIT_GLX” in the Sender table column, and “HKONT” in the Sender field column. Save your entries and return to the activity assignment screen.
Assign the Posting indicator “1 Activity/ledger is posted directly (not subsequently)”.
Set the Write line items indicator.
Save your entries.
Choose the Ledger selection pushbutton. On the Change Ledger: Ledger Selection screen, choose the F4 Help for the Condition field. You may get the error message “You are using interpreted rules”. In this case, go to the message long text and choose the link Convert.
This takes you to the Change Rules: Overview screen. Click on the Create Rule pushbutton to get to the Create Rule: New Rule screen. Enter a name for the rule, for example, “TRM_SLACTIV – Activate TRM Postings”. Save your entries and branch to the rule definition via the tree structure.
In the menu, choose Settings -> Expert Mode and enter the following rule in the editor:ACCHD-ACC_PRINCIPLE = ‘X X X X’
where X X X X = the name of the accounting principle to be updated to this ledger.
You can also generate this rule content without activating the expert mode. On the tab page Table Fields, double-click on “FI: Interface to Accounting: Header Information”. Search for the Accounting Principle field using the magnifying glass. Double-click on the field. Choose the pushbutton #=#, followed by the Constant button, and enter the accounting principle in the dialog box.
Save your entries.
Return to the special ledger definition.
- k) Save your entries again, and exit the special ledger definition.3. You can create any other special ledgers you require in the same way, or create copies of the first one and adapt them accordingly.
Activities
- Choose New Entries.2. Choose the accounting code and assign a valuation area.3. In the Valuation Area – Additional Data section, enter the relevant valuation currency and the rate type to be used for currency translation if the operative application is unable to supply the amount in valuation currency.4. In the Data Transfer to Accounting section, you specify how the data for the parallel valuation areas is to be updated.
The following options are available:a) Do not post to FIb) Post to FI
If you decide to update FI, you must specify an accounting principle. Accounting principles are defined in the Customizing settings for FI and contain information on whether data is written to a special ledger, and, if this is the case, which special ledger is used (IMG path: Financial Accounting -> Financial Accounting Global Settings -> Company Code -> Parallel Valuation Methods -> Accounting Principles and Additional Ledgers).
H- Define and Assign Valuation Classes
SPRO> Financial Supply Chain Management> Treasury and Risk Management> Transaction Management> General settings> Accounting> Setting for Position Management> Define and Assign Valuation Classes
We define general valuation classes (GVCs) and special valuation classes for each valuation area and assign these classes to each other.
Note:
- The valuation classes are valuation-independent; that is, the assignment of the valuation class alone provides no information on the valuation of these positions . In the IMG activity ‘Assign Position Management Procedure’, you define the rules for assigning position management procedures to positions. The valuation class is one of the criteria that you can use to assign the position management procedure.
- The special valuation class is a fixed differentiation criterion for adapting the subledger positions.
You make the following settings in this IMG activity:
- Define general valuation classesOn an abstract level, the general valuation classes allow the trader in the front office to group the positions.a) Define a 4-digit short name and a long name for the general valuation class.b) Define whether the valuation class is used for the current portion of long term investments or not.Example: General valuation classes◦Long-Term Investment
◦Medium-Term Investment
◦Short-Term Investment
◦Current Portion of Long Term Investments
When purchasing 1000 shares, for example, the trader could determine to which GVC this position is to be assigned. This would represent a grouping at an abstract level.2. Define valuation classesHere the valuation classes are defined for each valuation area, it is implicitly defined how the balance sheet is to be structured.Example:
001 HGB Fixed assets
001 HGB Current assets
002 US-GAAP Held to Maturity (HtM)
002 US-GAAP Available for Sale (AfS)
002 US-GAAP Trading
- Assignment of general valuation class to valuation classExample:
short-term 001 Current assets
short-term 002 Trading
medium-term 001 Fixed assets
medium-term 002 Available for Sale (AfS)
long-term 001 Fixed assets
long-term 002 Held to Maturity (HtM)
If a trader in the front office has assigned a position to the GVC short-term (long-term), then the position is assigned to valuation class current assets (fixed assets) in valuation area 001 HGB, and to valuation class Trading (Held to Maturity) in valuation area 002 US-GAAP.
Further notes
- Assign General Valuation Class to Groups
- You can define proposals for assigning general valuation classes when entering transactions in Customizing under Securities / Listed Derivatives / OTC Derivatives -> Transaction Management -> Assign General Valuation Class.
I- Define Position Management Procedure
SPRO> Financial Supply Chain Management> Treasury and Risk Management> Transaction Management> General settings> Accounting> Setting for Position Management> Define Position management Procedure
We define the position management procedures you require. In these you establish the rules for maintaining the positions, for example, how the positions are to be valued, and also how the derived business transactions are to be generated in the case of position outflows or balance sheet transfers.
In the Customizing activity Assign Position Management Procedure, you determine the rules for assignment of position management procedures to positions.
Under Assign Update Types for Valuation and under ‘ Assign Update Types for Derived Business Transactions, you then define for each position management procedure, which update types are to be generated for carrying out the key date valuation and also which are to be used for derived business transactions in the case of position outflows and balance sheet transfers.
Example
Position management procedure: 1000 for SE/Loan: Mark-to-Market (P/L) / Amortization (SAC Net)
Position management category: Sec./Loans/M.Mkt/List.Opts Norm.Style.(w/o index-link.bonds)
Transfer category: Only Post to Used Components
Step 1: Amortization with LAC net procedure
Step 2: Security valuation with Mark-to-Market procedure
Step 3: Foreign currency valuation with Mark-to-Market procedure
For all steps, the indicator Carry Out for Key Date Valuation is set.
Requirements
The valuation procedures must have been defined in the following Customizing activities:
- Define Amortization Procedure
- Define One-Step Price Valuation Procedure
- Define Securities Valuation Procedure
- Define Foreign Currency Valuation Procedure
- Define Price Valuation Procedure for Forward Exchange Transactions
You can find the Customizing activities under Transaction Manager -> General Settings -> Accounting -> Settings for Position Management -> Key Date Valuation.
Standard settings
Various position management procedures have been defined in sample Customizing.
Activities
- Choose New Entries.2. Assign a short and long text for the position management procedure.3. Select the position management category.4. Select the transfer category.◦Value ‘Standard’: In transfers, the values of the source position components are transferred to the corresponding components of the target position.
◦Value Post to Same Components:
During transfers, the values from the source position components are transferred to the equivalent target position components.◦Value Only Post to Used Components:
In transfers, the only components filled in the target position are those that are held according to the position management procedure.5. Determine which steps are to be carried out and in which sequence. In each case, choose a procedure. If the indicator Perform for Key Date Valuation is set, then the step is carried out during a key date valuation.The sequence of the steps is taken into account when exchange rate gains are being calculated.Note that if you’re performing hedge accounting for foreign exchange risks (P-Hedge Accounting), you have to determine a step for Security Valuation with the corresponding procedure Security Valuation for Hedge Accounting (FX Risk).6. Save your entries.
J- Assign Position Management Procedure
SPRO> Financial Supply Chain Management> Treasury and Risk Management> Transaction Management> General settings> Accounting> Setting for Position Management> Assign Position management Procedure
You control the assignment of the position management procedures using the parameters accounting code, valuation area, valuation class, product category, product type, transaction type, portfolio, and security account group.
You can work with initial entries, that is, you could choose a position management procedure for valuation class ’01’ without specifying the other factors. The selected position management procedure is then assigned to all positions with valuation class ’01’ unless there are other suitable entries for which the remaining factors to the right side in the assignment table are specified.
The general determination algorithm works as follows:
First, for a position specified by accounting code, valuation area, valuation class, product category, product type, transaction type, portfolio and securities account group, all records are determined that are compatible with the position.
Second, the most suitable entry is chosen.
Recommendation
We recommend making an initial entry for a default position management procedure, that is, leaving all factors with initial values. This position management procedure will then always be used if no other entry can be matched with the predefined influencing factors This prevents a situation arising where no position management procedure is found.
Conclusion
In the TRM module, these organizational configurations are present. These configurations are necessary for us to create any deal. These customizations must be made for every company code. For new learners, this blog will be of assistance.
Cheers














Be the first to comment